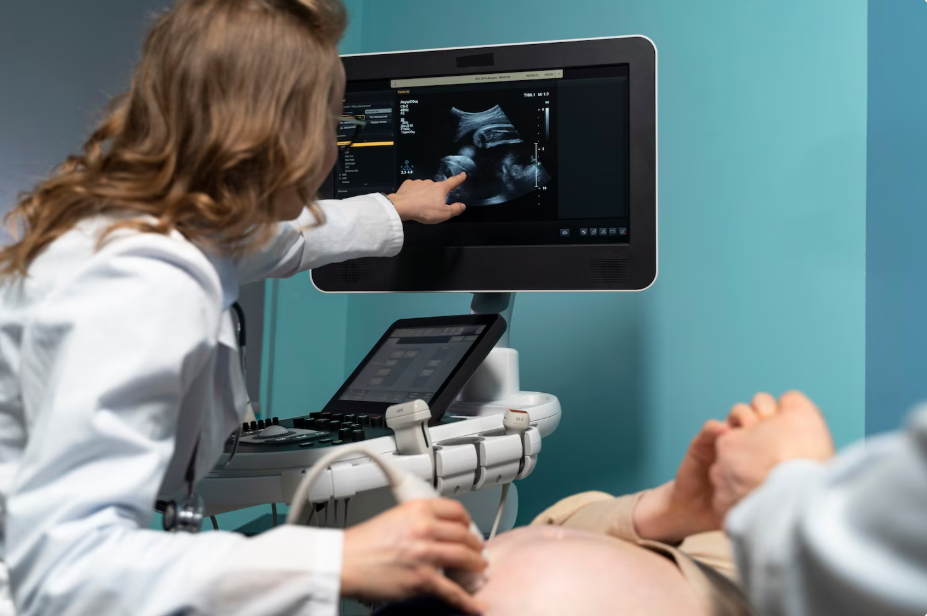
Pregnancy is a significant life event marked by physical, emotional, and medical milestones. One central component of prenatal care for many expectant parents is ultrasound imaging, a technique that uses sound waves to create visual representations of a developing fetus inside the womb. Beyond its role in medical monitoring, ultrasound imaging also allows families to observe fetal development, build understanding, and preserve meaningful moments throughout pregnancy.
What Is Ultrasound Imaging in Pregnancy
Ultrasound, also known as sonography, is a non-invasive imaging method that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of internal structures. During pregnancy, ultrasound imaging creates real-time visuals of the fetus, placenta, and surrounding tissues. A handheld device called a transducer emits sound waves that travel through the body and reflect back, allowing a computer system to generate images on a screen.
Ultrasound technology is widely used because it does not involve radiation and is considered safe when performed appropriately. Imaging can be conducted through the abdomen and, in early pregnancy, may also involve internal imaging for clearer results.
Types and Timing of Prenatal Ultrasounds
Ultrasound imaging is performed at different stages of pregnancy, depending on medical needs and personal preferences. Some scans are part of routine prenatal care, while others focus on visual documentation and keepsake imaging.
Early Pregnancy Scans
In early pregnancy, ultrasound imaging is commonly used to confirm the presence of a viable pregnancy. These scans may identify the fetal heartbeat, estimate gestational age, and determine whether there is more than one fetus. Early imaging helps establish a baseline for prenatal care and assists healthcare providers in planning future monitoring.
Mid-Pregnancy Anatomy Scans
A detailed anatomy scan is typically performed during the middle of pregnancy. This scan allows for observation of fetal growth and development, including the structure of major organs and body systems. Measurements taken during this stage help assess whether development is progressing as expected and provide information about the placenta and amniotic fluid.
Advanced 3D and 4D Ultrasound Imaging
In addition to standard two-dimensional imaging, advanced ultrasound technologies such as three-dimensional (3D) and four-dimensional (4D) imaging offer more detailed visuals. 3D imaging creates lifelike still images by combining multiple angles, while 4D imaging adds real-time movement. These scans can show facial features, expressions, and movements, often providing a more comprehensive visual experience later in pregnancy.
Medical and Personal Uses of Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging serves both clinical and experiential purposes during pregnancy.
Medical Monitoring
From a medical standpoint, ultrasound is an essential diagnostic tool. It helps healthcare providers monitor fetal growth, evaluate organ development, estimate due dates, and detect potential complications. Ultrasound findings guide clinical decisions and may indicate whether additional monitoring or testing is needed.
Personal Understanding and Connection
For many expectant parents, ultrasound imaging also plays a personal role. Seeing visual images of the developing baby can make the pregnancy feel more tangible. Observing movements or features may strengthen emotional connection and help families better understand fetal growth stages.
What to Expect During an Ultrasound Session
A typical ultrasound session involves applying a gel to the abdomen to improve sound wave transmission. The transducer is then moved across the skin to capture images. The process is usually painless and takes between 15 and 45 minutes, depending on the type of scan.
During the session, individuals may see various aspects of fetal development, including heartbeat, movement, and body structure. Advanced imaging sessions may allow for longer viewing times and multiple angles, particularly later in pregnancy.
Understanding Ultrasound Cost and Planning
The cost of ultrasound imaging can vary depending on several factors, including location, type of scan, and whether the procedure is part of routine medical care. Standard ultrasounds ordered by healthcare providers are often covered by insurance plans, though out-of-pocket costs may apply depending on deductibles or coverage limits.
Additional imaging sessions, such as advanced 3D or 4D ultrasounds or elective scans outside of standard medical care, may involve separate fees. Understanding ultrasound cost in advance can help expectant families plan financially and decide which imaging options align with their needs and preferences.
Keeping a record of ultrasound appointments, including dates, purpose, and associated costs, can be helpful for budgeting and insurance documentation throughout pregnancy.
Including Family and Preserving Images
Ultrasound sessions may offer opportunities to involve family members, such as partners or relatives, allowing them to share in the experience. Viewing images together can be a meaningful moment and may contribute to shared anticipation and emotional support.
Images and videos from ultrasound sessions are often preserved as keepsakes. These visuals may be placed in pregnancy journals, baby books, or digital archives, providing a lasting record of fetal development stages.
Conclusion: The Role of Ultrasound in Pregnancy
Ultrasound imaging is a widely used and valuable part of the pregnancy experience. It supports medical monitoring while also offering insight into fetal development through visual representation. By understanding the types of ultrasound imaging available, what to expect during sessions, and general cost considerations, expectant parents can approach prenatal imaging with clarity and confidence.
Ultrasound serves as both an informational and experiential tool, helping individuals navigate pregnancy with greater awareness while preserving moments that many families treasure long after pregnancy has ended.